
Titanium is a metal that unites a number of useful properties such as lightweight, ductility, chemical and temperature resistance, and mechanical strength. Titanium alloys are among the most important materials that are used in aviation, rocketry, shipbuilding, and military equipment. It exhibits low electrical and thermal conductivity and provides great durability.
Order in Titanium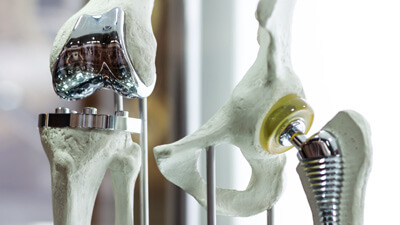



| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Service temperature | -328°F (-200°C) and 660°F (350°C) * |
| Density | 4.429 g/m³ |
| Tensile strength | 1100 MPa |
| Elastic Modulus | 120 GPa |
| Fatigue strength | 600 MPa |
* Ti-6Al-4V
Titanium is used across a vast number of industries, most notably in aviation, military, and space. Titanium alloys are nearly as strong as stainless steel but are much more lighter (by about 45%). At the same time, they are slightly heavier than aluminium, but almost twice as strong. Ti-6Al-4V (contains 6% Aluminium and about 4% Vanadium) is one of the most common titanium alloys thanks to corrosion resistance, high strength, and lightweight. It can be used both for aerospace and medical applications.
Furthermore, such alloy has outstanding heat and chemical resistance and is bio-compatible, which means that it can be used in healthcare (precisely speaking Ti-6Al-4VEli version of this alloy as it has Extra Low Interstitials) ideally for implants and prosthetics.
For metal 3D printing processes like DMLS, SLM, and EBS, the powder of Ti6Al4V alloy is used. It has a particle size of between 45 and 100 microns. Thanks to the vast opportunities of additive manufacturing, this material is used for creating complex parts and customized implants. 3D printed titanium parts are strong and relatively durable, though, they will appear weaker and more porous compared to machine or formed ones.
Titanium alloys, including 6Al4V, are quite hard for machining. However, with the proper procedures in place, titanium can be fabricated using techniques no more difficult than those used for machining stainless steel.
Titanium can be laser cut and marked. Cutting of titanium foils delivers a greyish edge and quite precise details.
Titanium can be formed through both cold and hot methods. If proceeding with the cold method, it should be taken into consideration that springback, galling, and cracking can occur during the process. Additionally, parts are recommended to undergo secondary surface treatment after cold forming. However, cold forming wins in terms of short cycle times.
Hot forming of titanium, on the other hand, provides certain advantages such as consistent wall thicknesses and virtually no springback or cracking but requires high grade equipment.
Steel is stronger than titanium and is the preferred option when strength is important and the weight doesn't really matter. Titanium is preferred where a lightweight and strong material is required. It can withstand very high and very low temperatures.
According to DemolitionRanch, the titanium plate can withstand little pellet guns all the way up to armor piercing .50 caliber black tip bullets.
Titanium is a weak conductor of electicity and heat.
Titanium is approximately 60% heavier than aluminum, but almost twice as strong.
全てのコメント (0)